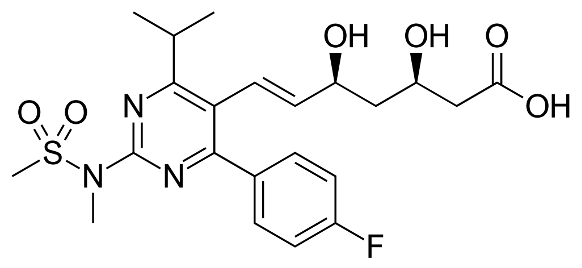
ESUVAST®– Rosuvastatine BP
COMPOSITION
5 Tablet: Each film coated tablet contains rosuvastatin Calcium BP equivalent to Rosuvastatin 5 mg
10 Tablet: Each film coated tablet contains rosuvastatin Calcium BP equivalent to Rosuvastatin10 mg
20 Tablet: Each film coated tablet contains rosuvastatin Calcium BP equivalent to Rosuvastatin20 mg
PHARMACOLOGY
Rosuvastatin is a selective and competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3 -methylglutaryl coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor of cholesterol. Rosuvastatin produces its lipid-modifying effects in two ways. First, it increases the number of hepatic LDL receptors on the cell surface to enhance uptake and catabolism of LDL. Second, Rosuvastatin inhibits hepatic synthesis of VLDL, which reduces the total number of VLDL and LDL particles.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption
Peak plasma concentrations of Rosuvastatin were reached 3 to 5 hours following oral dosing. Both peak concentration (Cmax) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) increased in approximate proportion to Rosuvastatin dose.
Distribution
Mean volume of distribution at steady-state of Rosuvastatin is approximately 134 liters. Rosuvastatin is 88% bound to plasma proteins, mostly albumin.
Metabolism
Rosuvastatin is not extensively metabolized. The major metabolite of Rosuvastatin is N- desmethyl rosuvastatin which has approximately one-sixth to one-half of the HMG- CoA reductase inhibitory activity of rosuvastatin. Overall, greater than 90% of active plasma HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity is accounted by Rosuvastatin.
Elimination
Following oral administration, Rosuvastatin and its metabolites are primarily excreted in the feces (90%). The elimination half-life (t½) of Rosuvastatin is approximately 19 hours.
INDICATION
Primary hypercholesterolaemia (type IIA including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia), mixed dyslipidaemia (type IIb), or homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia in patients who have not responded adequately to diet and other appropriate measures; prevention of cardiovascular events in patients at high risk of a first cardiovascular event.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Heterozygous Hypercholesterolemia (Familial and Nonfamilial) and Mixed Dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Type IIA and IIB): The usual recommended starting dose of Rosuvastatin is 10 mg once daily. Initiation of therapy with 5 mg once daily may be considered for patients requiring less aggressive LDL-C reductions or who have predisposing factors for myopathy. For patients with marked hypercholesterolemia (LDL- C > 190 mg/dl) and aggressive lipid targets, a 20 mg starting dose may be considered. The 40 mg dose of Rosuvastatin should be reserved for those patients who have not achieved goal LDL-C at 20 mg. After initiation and/or upon titration of Rosuvastatin, lipid levels should be analyzed within 2 to 4 weeks and dosage adjusted accordingly. Homozygous Hypercholesterolemia (Familial) The recommended starting dose of Rosuvastatin is 20 mg once daily in patients with homozygous FH. The maximum recommended daily dose is 40 mg. Rosuvastatin should be used in these patients as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g., LDL apheresis) or if such treatments are unavailable.
Dosage in Asian Patients:
Initiation of Rosuvastatin therapy with 5 mg once daily should be considered for Asian patients.
Use with Cyclosporine, Lopinavir/Atazanavir & Ritonavir:
In patients taking Cyclosporine, the dose of Rosuvastatin should be limited to 5 mg once daily. In patients taking Lopinavir and Ritonavir or Atazanavir and Ritonavir the dose of Rosuvastatin should be limited to 10 mg once daily.
SIDE EFFECT
Rosuvastatin is generally well tolerated. The most frequent adverse events thought to be related to Rosuvastatin were myalgia, constipation, asthenia, abdominal pain, and nausea.
PRECAUTION
Hypothyroidism should be managed adequately before starting treatment with a statin (Patients with hypothyroidism should receive adequate thyroid replacement therapy before assessing the requirement for lipid-regulating treatment because correcting hypothyroidism itself may resolve the lipid abnormality. Untreated hypothyroidism increases the risk of myositis with lipid-regulating drugs). Statins should be used with caution in those with a history of liver disease or with a high alcohol.
There is little information available on a rational approach to liver-function monitoring; however, a NICE guideline suggests that liver enzymes should be measured before treatment, and repeated within 3 months and at 12 months of starting treatment, unless indicated at other times by signs or symptoms suggestive of hepatotoxicity. Those with serum transaminases that are raised, but less than 3 times the upper limit of the reference range, should not be routinely excluded from statin therapy. Those with serum transaminases of more than 3 times the upper limit of the reference range should discontinue statin therapy.
Statins should be used with caution in those with risk factors for myopathy or rhabdomyolysis; patients should be advised to report unexplained muscle pain; patients of Asian origin; max. Dose 20 mg in patients with risk factors for myopathy or rhabdomyolysis (including personal or family history of muscular disorders or toxicity).
Hepatic impairment:
Statins should be used with caution in those with a history of liver disease and avoided in active liver disease or when there are unexplained persistent elevations in serum transaminases.
Renal impairment:
Initially 5 mg once daily (do not exceed 20 mg daily) if eGFR 30–60 ml/minute/1.73 m3; avoid if eGFR less than 30 ml/minute/1.73 m3
CONTRAINDICATION
Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to any component of this product. Rosuvastatin is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or with unexplained persistent elevations of serum transaminases.
DRUG INTERACTION
Erythromycin: Co-administration of Erythromycin with Rosuvastatin decreased AUC and Cmax of Rosuvastatin by 20% and 31%, respectively.
Itraconazole: Itraconazole resulted in a 39% and 28% increase in AUC of Rosuvastatin after 10 mg and 80 mg dosing, respectively.
Fluconazole: Co-administration of Fluconazole with Rosuvastatin resulted in a 14% increase in AUC of Rosuvastatin.
Warfarin: Co-administration of Warfarin (25 mg) with Rosuvastatin (40 mg) did not change Warfarin plasma concentrations but increased the International Normalized Ratio (INR).
Gemfibrozil: Co-administration of Gemfibrozil (600 mg twice daily for 7 days) with Rosuvastatin (80 mg) resulted in a 90% and 120% increase for AUC and Cmax of Rosuvastatin, respectively.
Antacid: Co-administration of an antacid (aluminum and magnesium hydroxide combination) with Rosuvastatin (40 mg) resulted in a decrease in plasma concentrations of Rosuvastatin by 54%.
Oral contraceptives: Co-administration of oral contraceptives (Ethinyl Estradiol and Norgestrel) with Rosuvastatin resulted in an increase in plasma concentrations of Ethinyl Estradiol and Norgestrel by 26% and 34%, respectively.
USE IN PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
Rosuvastatin should be administered to women of childbearing age only when such patients are highly unlike to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, therapy should be discontinued immediately.
Breast-feeding: It is not known whether Rosuvastatin is excreted in human milk.
STORAGE
Store tablet and powder for suspension at or below 30°C. Protect from light & moisture. Keep out of the reach of children.
PACKAGING
ESUVAST®: Tablet 5 mg: Each box contains 20/30/50 tablets in Alu-Alu blister pack.
ESUVAST®: Tablet 10 mg: Each box contains 20/30/50 tablets in Alu-Alu blister pack.
ESUVAST®: Tablet 20 mg: Each box contains 20/30/50 tablets in Alu-Alu blister pack.